What Is eSIM? A 2025 Guide With All You Need To Know


If you’ve ever fumbled with a SIM card, poked at your phone with a paperclip, or panicked when switching carriers mid-travel, you know the frustrations that come with those tiny pieces of plastic.
Now, there’s a better way to connect: eSIM.
eSIMs ditch the plastic and let you activate a mobile plan straight from your device. You can activate service instantly, switch networks without touching your hardware, and manage multiple lines from one device.
And as more devices drop the SIM card slot entirely (or at least add eSIM functionality), understanding how eSIMs work is something every mobile phone user should be familiar with.
So, what is eSIM? This guide will walk you through it. We will explore the three most user-friendly methods for remotely activating an eSIM-equipped consumer device, including smartphones, tablets, connected PCs, and smartwatches.
Understanding these activation methods is critical as they form the foundation of the eSIM's ability to provide users with a smooth, uninterrupted experience.
What Is eSIM?
Swapping SIM cards used to be a rite of passage—poke the tray, pray it ejects, and hope you don’t drop that fingernail-sized chip.
It’s not exactly elegant, but it gets the job done—until mobile technology evolved past the need for physical parts.
That evolution gave us the eSIM.
Now, to answer your burning question, “What is eSIM?”
An eSIM, short for embedded SIM, is a small chip soldered directly into your phone or device. It works just like a traditional SIM card. It connects you to a wireless carrier and enables phone calls, texts, and data.
However, there’s no card to insert, no tray to open, and no plastic to lose. You activate a mobile plan digitally, right from your settings.
This convenience is one of the reasons why eSIM adoption is accelerating. In 2025, an estimated 850 million smartphones will connect via eSIMs. That number is expected to reach at least 6.7 billion by 2030 (Source: GSMA Intelligence)
This “Big Bang” for mobile operators is more than just a technological upgrade; it represents the digitalization of connectivity distribution. As such, the eSIM promises to deliver an even higher level of customer experience, reducing the friction associated with traditional SIM cards and offering more seamless integration into the user’s digital lifestyle.
How Does an eSIM Work?
So, now that we’ve covered the question, “What is eSIM?” let’s take a closer look at how it works behind the scenes.
Instead of popping in a physical SIM card, your phone downloads something called a profile. Think of it like installing an app that contains your mobile details. These include your phone number, carrier information, and everything it needs to connect to a network.
This download happens over the air. Scanning a QR code or using your carrier’s app usually triggers it. Once you install the profile, your phone is ready to make calls, send texts, and use data—just like it would with a physical SIM.

Behind the Scenes: The Technology
eSIM seems pretty simple on the surface. However, there’s a sophisticated system quietly powering it.
Every eSIM-enabled device includes a built-in chip called the Embedded Universal Integrated Circuit Card (eUICC).

Unlike a traditional SIM, the chip doesn’t lock your device to one carrier. It can securely store multiple profiles and lets users switch between them through software.
A carrier or third-party network provider operates a centralized platform that remotely installs your mobile profile, which is essentially the digital version of your SIM. This process is what we call remote SIM provisioning.
They send encrypted credentials over the air, which your phone verifies and installs in a secure area of the chip. From there, your phone knows how to connect to the correct network.
Here’s what the process looks like:
- Your phone requests a set of secure instructions.
- The carrier approves and delivers them.
- The eSIM follows these instructions to go live.
It’s a bit like downloading an app, but for your mobile network.
Key Components of the eSIM Ecosystem
To fully understand the eSIM activation process, it’s important to look at the core components of the eSIM architecture. These components play a pivotal role behind the scenes, ensuring the smooth functioning of eSIM technology:
- The Embedded SIM (eSIM): This is a secure hardware component that is built into the device itself. It acts as a storage medium for the eSIM profile, which contains all the necessary information for the device to connect to a mobile network.
- The eSIM Profile: This digital file stores the user's subscription and network settings. It allows users to seamlessly connect to the mobile network associated with the subscription, without the need for a physical SIM card.
- The Subscription Manager Data Preparation (SM-DP+): This is a subscription management platform operated by mobile networks. It securely downloads the eSIM profile onto the device once the user has purchased a subscription. After the operator creates the subscription, the SM-DP+ is notified, and the eSIM profile is prepared for download.
These three components form the backbone of the eSIM ecosystem and enable users to enjoy a frictionless, digital-first mobile experience.
Supported devices

eSIM support is showing up in everything from smartphones to smartwatches. Here’s a quick snapshot of where you’ll find it:
- iPhones: XS, XR, and all newer models
- Android flagships: Google Pixel, Samsung Galaxy S20 and newer, and other top-tier Android phones
- iPads: Most recent models, including iPad Pro, iPad Air, and iPad Mini
- Wearables: Apple Watch (Series 3 and later), Samsung Galaxy Watch, and other LTE-enabled smartwatches
Note: Support varies by carrier and region. Not sure whether your device is eSIM-ready? You can use this eSIM compatibility checker to find out.
eSIM vs. Physical SIM: What’s the Difference?
At a glance, eSIM and physical SIMs serve the same purpose. They connect your phone to a mobile network. But the key to defining eSIM is knowing the difference between how they do it.
With an eSIM, there’s no tiny card to swap, no tray to open, and no waiting for the mail. It’s instant, digital, and far more flexible.
Activation and Convenience
With a physical SIM, activating your phone means waiting for a SIM card to arrive in the mail or making a trip to the store.
With eSIM cards, things are much more seamless. You scan a QR code or follow a link in your carrier’s app. Then, your phone connects within minutes.
This is why 85% of users find eSIM activation effortless. (Source: Counterpoint)
Switching Providers
Switching mobile carriers used to involve logistics:
- Ordering a new SIM
- Waiting for delivery
- Physically swapping cards
Now, when traveling abroad, you can install a local eSIM plan in minutes, often before your plane even lands. Many services let you browse, purchase, and activate a plan directly from your phone.
Dual SIM Functionality
Many eSIM-capable phones support dual SIM mode—one eSIM profile and one physical SIM. That means you can carry two numbers on one mobile device.
For example, keep your personal number on a physical SIM and your work number on an eSIM.
Security Considerations
Losing a phone with a physical SIM can put your number and data at risk. A thief can remove the SIM and drop it into another phone, potentially gaining access or cutting off your service.
Understanding what eSIM is and how it works helps put those risks into perspective. Since there’s no physical card to remove, your device securely stores the profile.
So, if you lose or someone steals your phone, your carrier can remotely lock or erase the eSIM profile. This gives you more control and peace of mind.
Advantages of Using an eSIM
From instant setup to smoother international travel and better sustainability, eSIMs offer clear advantages over traditional SIM cards.
Here’s why so many are making the switch.
Instant Connectivity
With eSIM cards, you can buy a plan, scan a QR code, and connect in minutes. And you can do this anytime, anywhere.
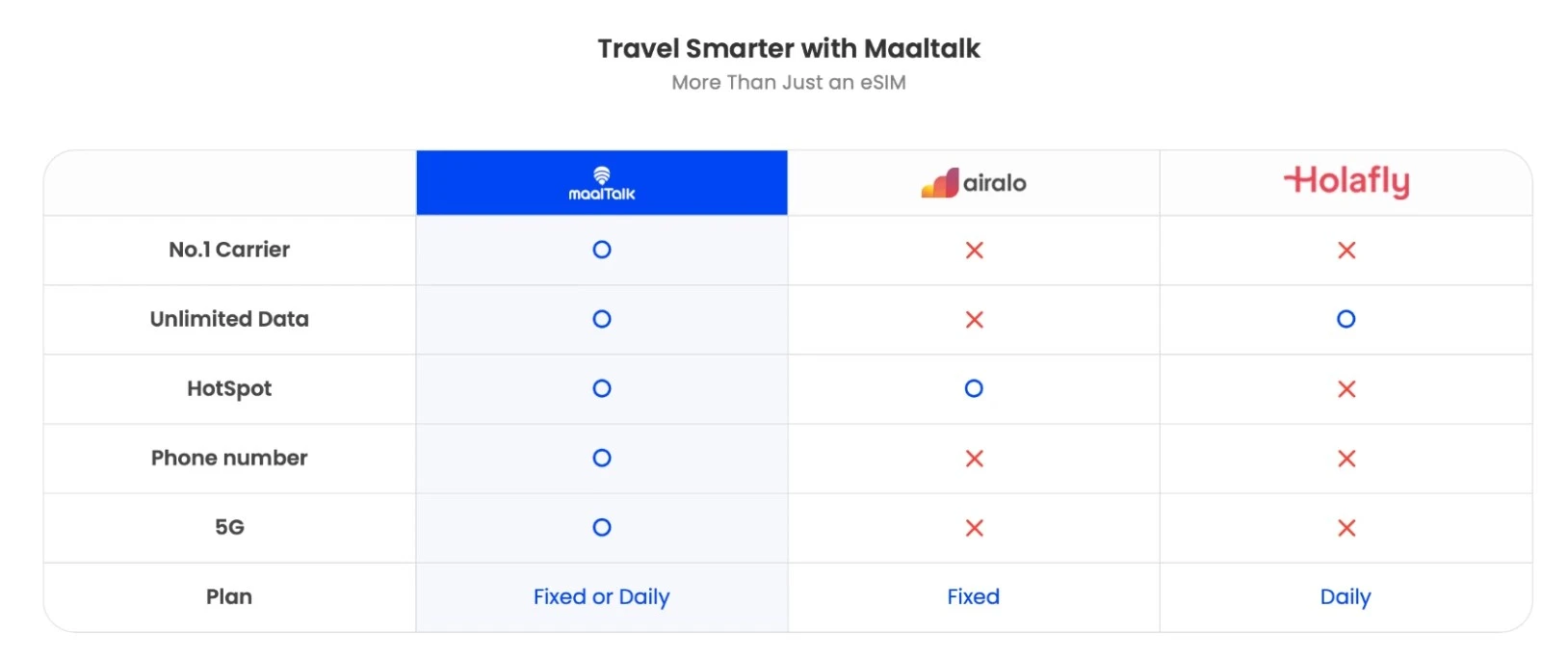
Great for Travelers
Skip roaming fees by downloading local or global data plans before you even land. Services like MaalTalk, Airalo, and Holafly make it easy to stay connected across multiple countries.
Eco-Friendly
eSIM reduces the need for physical SIM cards and packaging. This helps cut down on plastic waste.
Flexibility for Business Users
eSIM makes it easy to manage multiple numbers or carrier profiles from one device. For example, a sales rep can keep a local number in each region without carrying multiple phones.
How To Set Up an eSIM
Now that we have an understanding of what eSIM is, let’s explore the three main methods of activating eSIM-enabled consumer devices:
QR Code-Based eSIM Voucher Activation
One of the simplest and most commonly used methods to activate an eSIM is through a QR code.
When a user buys an eSIM-based mobile subscription, whether online or at a retail store, the mobile operator provides a digital QR code. The user can scan this QR code with their eSIM-capable device, triggering the download of the eSIM profile associated with the subscription.
This QR code contains important information, such as the SM-DP+ address, which guides the device to the operator’s platform to retrieve the correct eSIM profile.
It’s important to note that a primary internet connection (such as Wi-Fi) is necessary during this process to allow the device to communicate with the SM-DP+ server and complete the download of the eSIM subscription.
Manually Adding eSIM Activation Information
If you don’t have a QR code or otherwise need to manually activate an eSIM, the process is simple. First, locate the SM-DP+ address and activation code provided by your carrier. Then, open your cellular settings (on iPhone: Settings > Cellular or Mobile Data, on Android: Settings > Network & Internet).
Look for “Add eSIM” or “Add Cellular Plan.” You may need to select “Add Details Manually.”
Follow the prompts and enter your codes. Your phone will guide you through the process to complete the setup.
Carrier App eSIM Activation
Another increasingly popular method for eSIM activation is through a mobile network operator’s app. In-app eSIM activation offers a fully digital experience and can be an integral part of an operator’s eSIM-first strategy.
By incorporating eSIM activation directly into their app, mobile operators can create a streamlined user experience.
This method typically involves integrating an eSIM SDK (Software Development Kit) into the app, while a cloud orchestration layer manages the eSIM provisioning through APIs. Users can activate their eSIM, change devices, or upgrade their subscription all within the app, minimizing disruptions to their mobile service.
This approach also simplifies the back-end operations for mobile operators, making it an efficient and scalable solution.
By offering an entirely automated process, this method significantly enhances the user experience, making it easier for customers to manage their mobile subscriptions and devices.
Root SM-DS (Subscription Manager Discovery Service) eSIM Activation
The third method, the Root SM-DS (Subscription Manager Discovery Service), is a standardized solution for eSIM activation. It serves as a central hub, enabling devices to discover which SM-DP+ server holds their eSIM profile.
When a user purchases an eSIM subscription, the MNO informs the Root SM-DS of the available profile. The device can then query the Root SM-DS, which directs it to the appropriate SM-DP+ server to download the eSIM profile.
Major companies like Apple, Samsung, GSMA, and Google have already introduced their own Root SM-DS servers, with solutions such as Google eSIM Discovery for Android devices and GSMA eSIM Discovery for multi-brand compatibility.
Once the subscription is available, users receive a notification on their device, and the eSIM profile can be downloaded with a single tap.
Step-By-Step Setup
- Purchase an eSIM plan from MaalTalk’s website or app.
- Receive a QR code or eSIM activation information by email.
- Open your phone’s settings and navigate to the cellular or mobile data section.
- Scan the QR code using your camera or the built-in scanner in your settings, or manually add the eSIM information you received.
- Activate your profile, and you’ll be ready to connect.
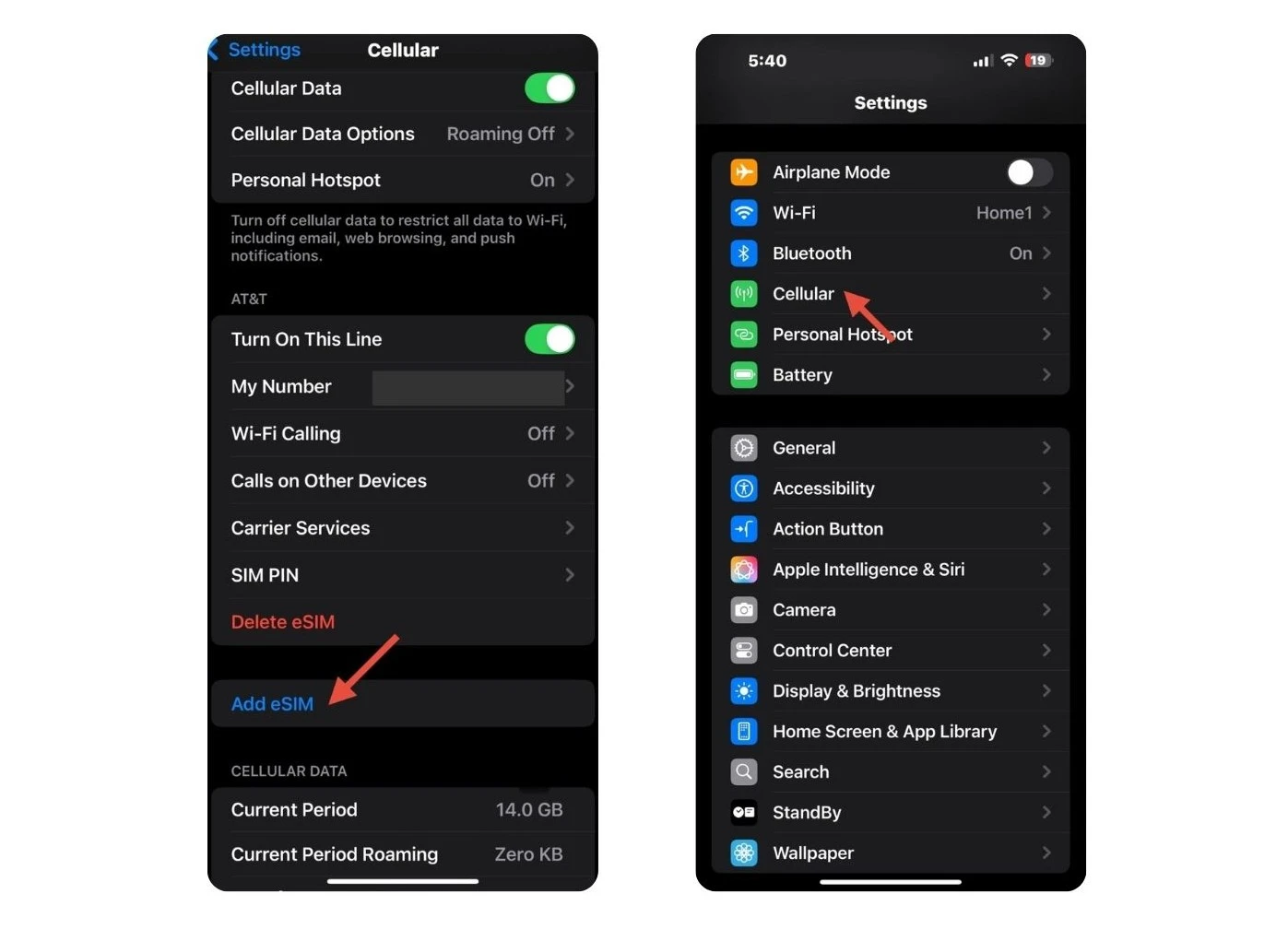
Setting up on iPhone
- Go to Settings > Cellular > Add eSIM.
Setting up on Android
- Go to Settings > Connections > SIM Card Manager > Add eSIM.
Troubleshooting Tips
If you run into issues, here are a few quick fixes:
- QR code not working: Make sure your device supports eSIM and that your carrier profile hasn’t expired.
- Profile not downloading: Double-check that your phone is carrier-unlocked and eSIM-compatible.
- No service after activation: Restart your phone and toggle airplane mode.
Conclusion: Simplify Your Mobile Life With eSIM
eSIM takes the unnecessary steps out of staying connected.
As eSIM adoption accelerates, the MaaltalkNow App emerges as a valuable tool for consumers, simplifying the process of managing eSIM profiles.
Through MaaltalkNow, users can buy and install their eSIMs, track their data usage and speed, and utilize all the AI features the app has to offer. These include:
- AI Product Recommendations
- Speed and Usage Tracker
- Maaltalk Smart Lens
- AI Travel Planner
- Travel Budget
- AI Agent
This kind of app-based eSIM management is essential for staying ahead in a landscape where billions of IoT (Internet of Things) devices are expected to come online in the coming years.
Want even more value? Enjoy a 10% discount on ALL eSIMs when you purchase through the MaaltalkNow app.
Are you ready to move on from physical SIM cards? Explore MaalTalk’s latest eSIM plans for 2025 and get started in minutes.
Frequently Asked Questions About eSIMs
Still have questions about eSIMs? We’ve got you covered.
Can I Use an eSIM and a Physical SIM Together?
Yes. Most eSIM-capable phones support dual SIM functionality.
What Happens if I Lose My Phone?
Your carrier can remotely lock or erase your eSIM to protect your data and number.
Are eSIMs Secure?
Yes, very. Manufacturers encrypt eSIM profiles, store them in a secure chip, and make them harder to tamper with than physical cards.
Can I Use an eSIM for Calls and Texts?
Yes. eSIM supports voice, text, and data—just like a traditional SIM.
Do eSIMs Work On Prepaid and Postpaid Plans?
Yes, they do. Most major carriers now offer both types of plans with eSIM compatibility.
Are eSIMs Permanent?
No. You can delete or replace an eSIM profile anytime through your device settings.



